First Class Tips About Is UEFI Firmware Settings Same As BIOS

UEFI Versus BIOS Hoe Verschillen Ze?
Decoding the Mystery
1. What's the Buzz About Firmware Anyway?
Alright, let's talk about something that sounds way more complicated than it actually is: firmware. Think of firmware as the software that makes your computer's hardware tick. It's the behind-the-scenes stuff that allows your keyboard to type, your mouse to click, and your screen to, well, screen. Now, the big question: Is UEFI firmware settings same as BIOS? The short answer? Not really, but they're related like cousins in the tech family.
BIOS, or Basic Input/Output System, has been around for ages. It's the traditional way computers started up and got their basic instructions. Imagine a really old instruction manual that everyone used to follow. UEFI, or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, is the new kid on the block, designed to replace BIOS and bring a whole bunch of improvements to the table. So, while they both handle similar tasks, they do it in vastly different ways.
Think of it like this: BIOS is a rotary phone, and UEFI is a smartphone. Both let you make calls, but one is a bit moreadvanced. UEFI offers a snazzier interface, supports larger hard drives, and can even boot your computer faster. It's like upgrading from dial-up to fiber optic internet.
Ultimately, the goal of both BIOS and UEFI is the same: to initialize the hardware and load the operating system. However, UEFI does it with modern conveniences and expanded capabilities, leaving BIOS in the technological dust.
UEFI
2. Why is UEFI the Cool Kid on the Block?
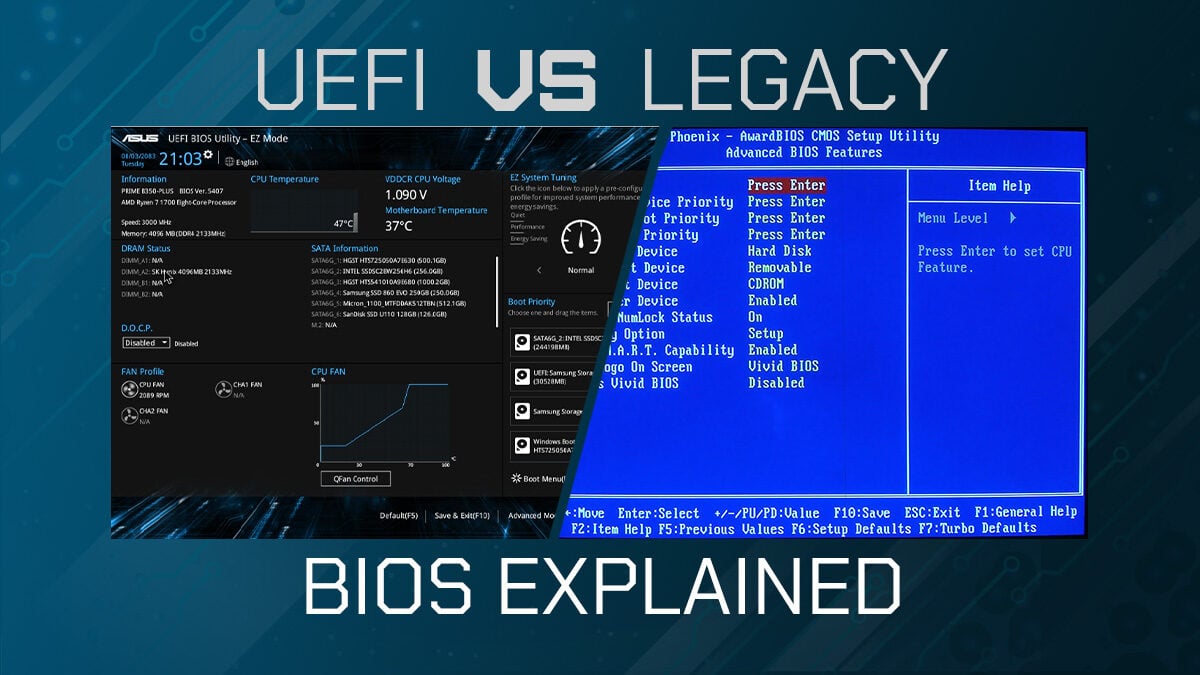
So, what makes UEFI so much better than the good old BIOS? Let's dive into some of the key features that have made UEFI the standard for modern computers. First up: graphical interface. Remember those clunky, text-based BIOS menus? UEFI throws those out the window with a slick, user-friendly interface that you can navigate with your mouse. It's like going from command-line to Windows — a massive upgrade.
Then there's support for larger hard drives. BIOS had a limitation of 2.2TB, which, in today's world of multi-terabyte storage, is practically nothing. UEFI can handle drives much, much larger, meaning you can finally store all those cat videos without worrying about running out of space. It also offers improved security features, such as Secure Boot, which helps prevent malware from hijacking your system during startup. This is akin to adding a security system to your home to protect against unwanted guests.
UEFI also supports faster boot times. Because it's designed to be more efficient, UEFI can start your computer quicker than BIOS. This means less waiting and more doing. Nobody likes waiting for their computer to boot up, right? And let's not forget about its modular design. UEFI is more flexible and adaptable, allowing manufacturers to add new features and functionalities more easily. It's like having a smartphone that gets regular software updates.
Consider UEFI as the evolution of computer startup, designed for modern hardware and security needs. Its graphical interface, expanded storage support, enhanced security, and faster boot times make it a significant upgrade over BIOS, ensuring a smoother and safer computing experience.

Uefi Bios Utilityadvanced Modewindows
BIOS
3. The Old Faithful, But Is It Enough?
Despite being superseded by UEFI, BIOS isn't completely obsolete. It still plays a role in older systems and even in some modern ones as a fallback. It's like that old, reliable car you keep around even after you've bought a shiny new one — it might not be the fastest or the flashiest, but it gets the job done in a pinch. BIOS is simple, straightforward, and well-understood. Its basic functionality remains essential for initializing hardware and starting the boot process.
One advantage of BIOS is its compatibility with older hardware and operating systems. If you're running a legacy system or an older version of Windows, BIOS might be your only option. Its also less complex than UEFI, making it easier to troubleshoot and configure for those who are comfortable with its text-based interface. However, its limitations in terms of storage capacity, security, and boot speed are becoming increasingly apparent in today's computing landscape.
Think of BIOS as a sturdy, dependable tool that has served us well for many years. While it may lack the advanced features and graphical interface of UEFI, it still has its place in the world of computing, particularly in older systems. It's like a classic car that, while not as fast or efficient as modern vehicles, still holds a certain charm and utility.
In simple terms, while UEFI offers a more advanced and secure computing experience, BIOS retains its relevance for older systems and users who prefer a simpler, more straightforward approach to hardware initialization and booting. It's a testament to its enduring design that it still finds a purpose even in the age of more sophisticated technology.
Key Differences
4. What Truly Sets Them Apart?
To really understand the difference between UEFI and BIOS, lets get down to the specifics. First and foremost, the interface is a major differentiator. BIOS uses a text-based interface that can be navigated with the keyboard, while UEFI boasts a graphical interface that supports mouse input. This makes UEFI much more user-friendly, especially for those who arent comfortable with command-line interfaces.
Another key difference lies in their boot processes. BIOS uses a Master Boot Record (MBR) partitioning scheme, which limits the size of hard drives it can support to 2.2TB. UEFI, on the other hand, uses the GUID Partition Table (GPT) partitioning scheme, which can support drives much larger than 2.2TB. This is crucial for modern computers that often use multi-terabyte storage devices. Furthermore, UEFI offers faster boot times due to its more efficient initialization process.
Security is another area where UEFI shines. It includes features like Secure Boot, which helps prevent malware from hijacking the boot process. This is a significant advantage over BIOS, which lacks built-in security measures against boot-level attacks. And lastly, consider the versatility. UEFI's modular design makes it more adaptable and allows for easier updates and feature additions, whereas BIOS is more rigid and less flexible.
In summary, the key distinctions between UEFI and BIOS lie in their interfaces, boot processes, storage support, security features, and overall versatility. UEFI offers a modern, user-friendly experience with improved security and support for larger storage devices, making it the preferred choice for modern computers. BIOS, while reliable, lags behind in these crucial aspects.
UEFI Vs BIOS What Is The Difference Between And UEFI?
So, Are They the Same? A Final Verdict
5. The Truth, the Whole Truth, and Nothing But the Truth
Alright, let's cut to the chase: Is UEFI firmware settings same as BIOS? No, they are not the same, but they serve a similar purpose. Think of BIOS as the horse-drawn carriage of computer startup processes, and UEFI as the sleek, modern sports car. Both get you where you need to go — booting up your computer — but one does it with a lot more style, speed, and added features.
While BIOS has been a reliable workhorse for many years, UEFI represents a significant step forward in terms of functionality, security, and user experience. UEFI's graphical interface, support for larger hard drives, faster boot times, and advanced security features make it the clear winner in today's computing landscape. So, while they both play a crucial role in the boot process, UEFI is the modern standard designed for the demands of today's hardware and software.
It's like comparing a black-and-white television to a high-definition smart TV. Both display images, but the quality and features are worlds apart. UEFI offers a more versatile and secure computing experience, ensuring your system starts up smoothly and stays protected against potential threats. BIOS, on the other hand, is more limited in its capabilities, though it still has its place in older systems.
Therefore, while UEFI firmware settings and BIOS both handle similar tasks, they are fundamentally different in their design, features, and capabilities. UEFI is the modern evolution of the boot process, offering a more efficient, secure, and user-friendly experience than its predecessor, BIOS. Embracing UEFI means embracing the future of computing.
FAQ
6. Everything You Always Wanted to Know...
Q: Can I upgrade from BIOS to UEFI?A: It depends on your motherboard. Some motherboards support both BIOS and UEFI, and you can switch between them in the firmware settings. However, if your motherboard only supports BIOS, you won't be able to upgrade to UEFI without replacing the motherboard.
Q: How do I access UEFI settings?A: Typically, you can access UEFI settings by pressing a specific key during startup, such as Delete, F2, F12, or Esc. The key varies depending on the motherboard manufacturer, so check your computer's manual or look for a prompt during startup.
Q: Is UEFI more secure than BIOS?A: Yes, UEFI is generally more secure than BIOS. It includes features like Secure Boot, which helps prevent malware from hijacking the boot process. This adds an extra layer of protection to your system and ensures that only trusted software is loaded during startup.
Q: What if my computer won't boot after changing UEFI settings?A: If your computer won't boot after changing UEFI settings, you can try resetting the UEFI settings to their default values. There is usually a button on the motherboard for this. Refer to your motherboard's manual for specific instructions on how to perform a CMOS reset.