Fantastic Tips About Is 220v 2-phase Or 3-phase

Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding Electrical Phases
Ever stared at an electrical outlet and wondered about the magic happening inside? Probably not, unless you're an electrician or have a penchant for pondering the inner workings of your toaster. But when it comes to higher voltage systems, like 220V, things get a bit more interesting. The question often pops up: is 220V two-phase or three-phase? Let's demystify this a little. The term "220V" itself simply refers to the voltage level. It's like saying you have a car; it doesn't tell you if it's a sedan or a truck. Similarly, 220V doesn't inherently dictate the number of phases. That's a separate characteristic.
In everyday language, we often use "220V" as a general term, but technically, in North America, you're more likely to find 240V in residential settings. Semantics aside, the core concept remains: voltage is just one piece of the puzzle. Think of it like this: voltage is the pressure of the water in a pipe, while the number of phases is like having multiple pipes feeding into the same source. More pipes (phases) can deliver more water (power) at a given pressure (voltage).
So, back to the original question. The real answer is that 220V (or more accurately, 240V) can be single-phase, two-phase (rare), or three-phase, depending on the specific application and electrical system design. It really depends on what is being use in that equipment and how the electric grid has been set up to supply it. Different situations will use different forms of electricity so it can be delivered safely and effectively.
The vast majority of residential uses for 220V (or 240V) appliances are single-phase. This might include your electric stove, clothes dryer, or water heater. These high-power appliances need more than the standard 120V outlet provides, but they don't require the complexities of a multi-phase system. This is also one of the easiest ways to supply that level of power to a home without needing a complete overhaul of the electrical system.

How To Convert 3 Phase 440 Volts Into Single 220 Volt Electrical
Two-Phase Systems
2. Exploring Obsolete Two-Phase Power
Let's address the two-phase elephant in the room. Two-phase power systems are, to put it mildly, pretty uncommon these days. They were used in some older industrial applications, particularly in the early days of AC power distribution, but they've largely been phased out (pun intended!) in favor of more efficient three-phase systems. Trying to find a modern two-phase setup is like searching for a cassette player in a self-driving car — technically possible, but highly improbable.
The main reason for their decline is efficiency. Three-phase systems are simply more efficient at delivering power and allow for simpler and more compact motor designs. Two-phase systems are also less balanced than three-phase, which can lead to increased voltage fluctuations and other issues. You'll be much more likely to encounter these systems as historical curiosities. A power museum would be more likely to have these systems than a current day power plant.
While two-phase might conjure images of vintage machinery humming away in some forgotten factory, the reality is that theyre essentially relics of the past. The benefits of three-phase power in terms of efficiency and reliability far outweigh any perceived advantages of the two-phase approach. In today's world, they're simply not a practical or economical choice for most applications.
Now, that doesn't mean they've completely vanished from the earth. Some specialized or legacy systems might still exist, but they're exceedingly rare. If you stumble upon one, consider yourself an electrical archaeologist — you've unearthed a piece of history! But for the vast majority of situations, you can safely assume that a 220V (or 240V) circuit is either single-phase or, more likely in industrial settings, three-phase.

Three Phase Electric Power
Three-Phase Power
3. Understanding the Power of Three-Phase
Enter three-phase power, the unsung hero of modern industry. This is where things get serious. Three-phase systems are the backbone of industrial power distribution, powering everything from massive motors to sophisticated manufacturing equipment. They're designed to deliver large amounts of power efficiently and reliably, making them ideal for demanding applications. Three-phase power is the strong, silent type of the electrical world.
The beauty of three-phase lies in its balanced nature. The three phases are offset by 120 degrees, which means that the power delivery is smooth and constant. This leads to more efficient motor operation, reduced vibration, and longer equipment life. It's like having three evenly spaced cylinders firing in an engine, providing a smooth and consistent flow of power. Try to imagine that in a big factory that needs to keep a lot of machines running non stop to keep production on target. A hiccup in power could be devastating!
In a three-phase system, you'll often see voltages around 208V, 240V, or 480V, depending on the specific application and local electrical codes. So, while you might encounter a 220V (or 240V) three-phase system, it's essential to recognize that it's just one possible voltage level within the broader spectrum of three-phase power. It all depend on the power grid and the type of machinery being used.
Think of it this way: if single-phase is like a bicycle, and two-phase is a rickshaw, then three-phase is a freight train. It's built for heavy lifting and designed to handle the most demanding power requirements. So, if you're dealing with industrial equipment, large commercial buildings, or any application that requires significant power, chances are you're looking at a three-phase system. Its efficient and reliable, making it suitable for most of the demands of a modern society.
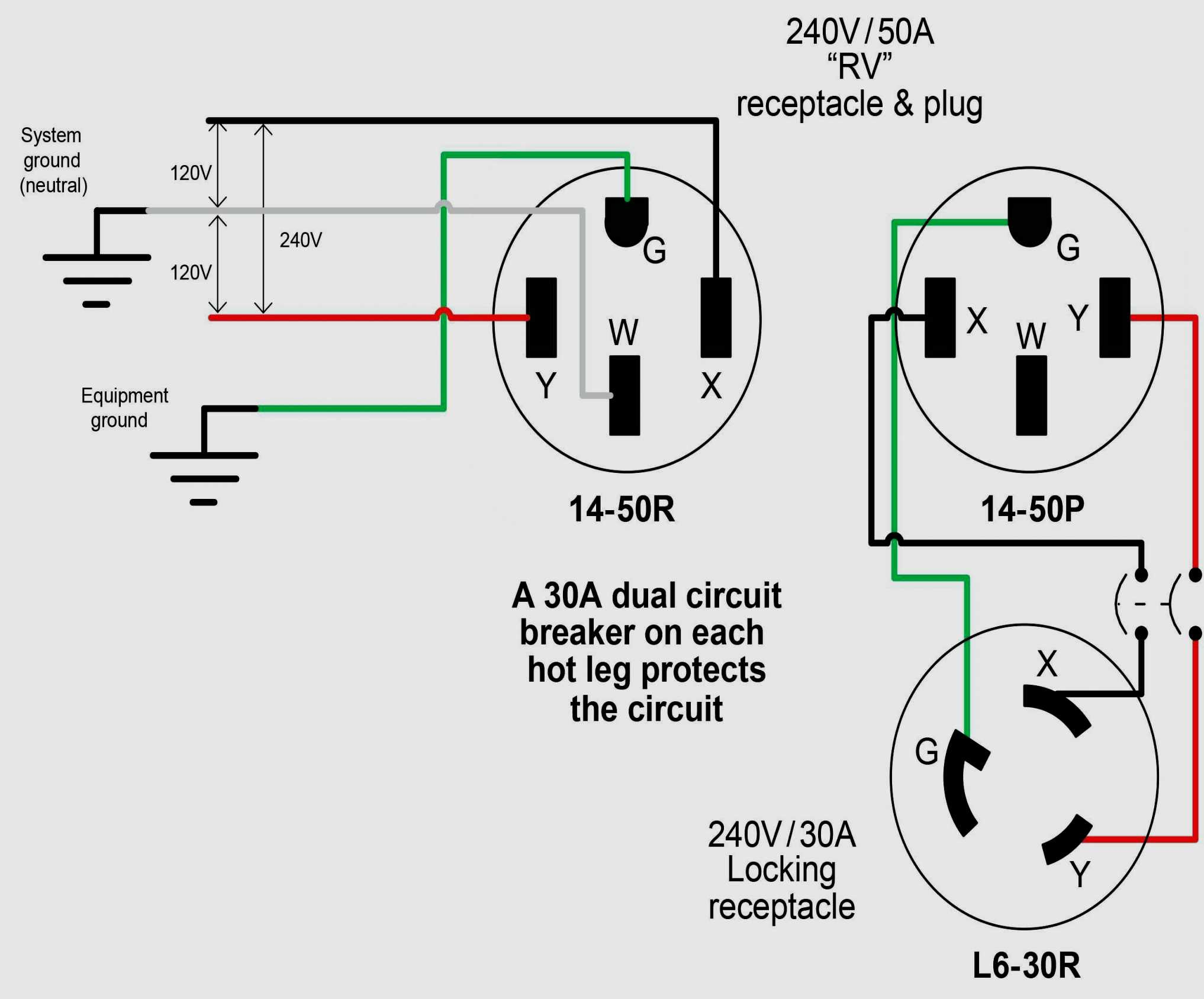
3 Phase 240v Wiring
Identifying Your System
4. Tips for Determining Electrical Phases
Alright, enough theory. How do you actually figure out whether you're dealing with single-phase, two-phase (unlikely), or three-phase power? Well, unless you're a qualified electrician, it's generally best to leave the hands-on investigation to the professionals. Messing with electrical systems can be dangerous, and it's always better to err on the side of caution. But here are a few clues that can help you get a sense of what you're dealing with.
First, check the breaker panel. In a residential setting, single-phase systems are the norm. You'll typically see a series of single-pole breakers (for 120V circuits) and double-pole breakers (for 240V circuits). A double-pole breaker takes up two slots in the panel and is often used for high-power appliances like stoves, dryers, and water heaters. In this case, its pretty common and standard so it is easy to identify.
Second, look at the equipment you're powering. If you're dealing with large industrial motors, heavy machinery, or commercial HVAC systems, it's almost certainly a three-phase system. These types of equipment require the higher power and efficiency that three-phase power provides. Often, you can find this information printed on the device near where the electrical cord is connected. However, always be careful and check with the manufacturer if you are not sure.
Finally, if you're unsure, consult a qualified electrician. They can use specialized equipment to measure the voltage and phase relationships in your electrical system and accurately determine the type of power you're dealing with. Remember, safety first! Don't take any unnecessary risks when working with electricity. A good electrician is worth every penny to ensure that the job is done safely and correctly.

Understanding 220V Single Phase Wiring A Diagram Guide
Why Does It Even Matter?
5. Understanding the Importance of Phase Identification
You might be wondering, "Okay, so it's single-phase or three-phase. Why should I even care?" Well, knowing the type of power system you're dealing with is crucial for several reasons. First and foremost, it ensures safety. Connecting equipment to the wrong type of power can be dangerous and can damage the equipment or even cause a fire. Think of it as trying to put diesel in a gasoline engine — it's not going to end well.
Secondly, proper phase identification is essential for proper equipment operation. Motors designed for three-phase power will not work correctly (or at all) on single-phase power, and vice versa. Mismatched power systems can lead to reduced efficiency, overheating, and premature equipment failure. Matching the correct power supply is important for efficiency and reliability of your machinery.
Furthermore, understanding the type of power system is critical for electrical system design and maintenance. Electricians need to know the phase configuration to properly size conductors, install protective devices, and troubleshoot electrical problems. Correct power matching can also extend the life of the machine, saving you time and money on repairs!
In essence, knowing whether you're dealing with single-phase, two-phase, or three-phase power is like knowing the language of electricity. It allows you to communicate effectively with your electrical system, ensuring that everything runs smoothly, safely, and efficiently. And while it might seem like a technical detail, it's a detail that can make all the difference.
